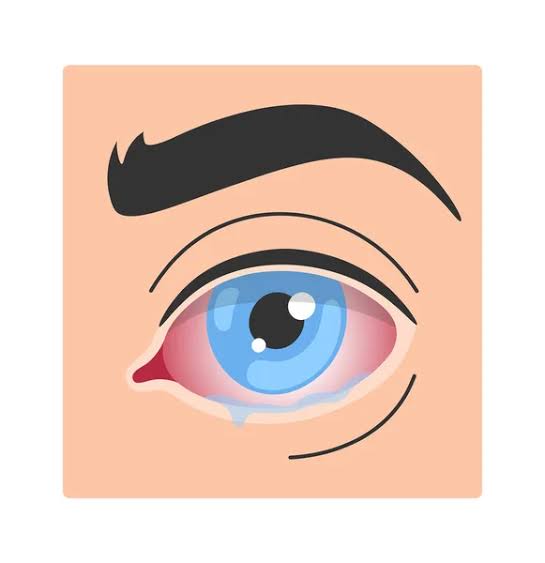
Keratitis is an eye condition that can be debilitating and painful for people of any age. The cornea, the transparent outer layer of the eye, is the subject of this condition. A healthy cornea is essential for clear vision, and any problems with it can cause pain, sensitivity to light, blurred vision, and other symptoms.

The Pathology of Keratitis
Keratitis can be brought on by a variety of things, like injuries, infections, or other health issues. Infections are perhaps the most well-known cause, with microorganisms and parasites being possible guilty parties. At the point when the cornea is compromised, it can become powerless to these microorganisms, prompting aggravation and resulting keratitis.
The Stages of Keratitis
There is no one-size-fits-all treatment for keratitis. It can occur in various stages, each with its own set of difficulties. The phases of keratitis include:
1. The top layer of the cornea is affected by superficial keratitis, which frequently causes tearing, redness, and discomfort.
2. When an infection or inflammation reaches a deeper level in the cornea, symptoms may get worse, leading to scarring and vision issues.
3. In this stage of neurotrophic keratitis, the cornea loses its sensitivity, which can result in corneal erosion that lasts for a long time along with other complications.
Causes of Keratitis
In order to prevent and treat keratitis, it is essential to comprehend its causes. The causes include:
1. Infections: Keratitis can be brought on by bacterial, viral, fungal, or parasitic infections.
2. Corneal Injuries: The cornea can be damaged and inflamed by trauma, scratches, or foreign objects.
3. Dryness: The cornea can become dry and vulnerable if the eyes do not produce enough tears. This condition is known as dry eye syndrome.
4. Fundamental Medical Issues: Illnesses related to the immune system or lack of vitamin A can expand the gamble of keratitis.
Risk Factors of Keratitis
A few elements can make a patient powerless to keratitis. These include:
1. Contact Lens Use: Wearing contact lenses, particularly when it is not appropriately cleaned and kept up with, can expand the gamble of infection.
2. Impairment of Immune Function: People who have weaker immune systems are more likely to get infections that can cause keratitis.
3. Lack of Cleanliness: Unfortunate eye cleanliness practices can acquaint harmful microorganisms with the eye, prompting infections.
4. Ecological Variables: Exposure to residue, wind, and bright (UV) light can increase the risk of keratitis.
Signs and Symptoms of Keratitis
Perceiving the signs and side effects of keratitis is fundamental for early conclusion and treatment. Some typical signs include:
1. Eye Redness: Common signs of inflammation include pink or bloodshot eyes.
2. Eye Pain: Patients frequently describe a gritty or foreign body sensation with moderate to severe pain.
3. Excessive Tearing: The body’s natural response to irritation in the eyes is to tear more.
4. Sensitivity to Light: One of the most common signs of keratitis is photophobia, or sensitivity to light.
5. Blurry Vision: Vision can become hazy or blurry as the cornea is affected.
6. Foreign Body Sensation: Even though there is no visible foreign object, patients may experience the sensation that something is in their eye.
Differential Diagnosis for Keratitis
A differential diagnosis is important because keratitis and other eye conditions share some similarities. Conjunctivitis, uveitis, and dry eye syndrome are all conditions that have the potential to resemble keratitis. For a precise diagnosis, a thorough examination and review of the patient’s medical history are necessary.
Investigations of Keratitis
At the point when a patient presents with side effects demonstrative of keratitis, different examinations are fundamental for affirming the finding. Some examples include:
1. Slit Lamp Examination: An eye doctor examines the cornea with a slit lamp, which enables detailed observation of any lesions or inflammation.
2. Corneal Culture: A corneal tissue culture can be taken to determine the specific pathogen that is causing the infection.
3. Measurement of Intraocular Pressure: This test helps rule out conditions like glaucoma, which can look like some of the symptoms of keratitis.
4. Visual Acuity Test: The patient’s visual acuity can be used to determine the condition’s severity.
5. Fluorescein Staining: This symptomatic instrument helps feature corneal scraped areas or ulcers.
General Management of Keratitis
Keratitis management varies based on the cause, stage, and particular symptoms. Notwithstanding traditional medicines endorsed by a medical services proficient, corresponding and elective treatments can assume a strong part in overseeing keratitis. One such correlative methodology is homeopathy.
What Is Homeopathy?
Homeopathy is a holistic approach to medicine that focuses on boosting the body’s own natural healing mechanisms in order to address the underlying cause of a condition. Natural substances are repeatedly diluted and succussed (vigorously shaken) to make homeopathic remedies. The idea is that substances that have been greatly reduced can elicit a healing response in the body.
The Role of Homeopathy in Keratitis Management
While homeopathy is certainly not a substitute for traditional clinical treatment, it can supplement by giving an all encompassing way to deal with wellbeing. Homeopathic remedies may support the healing process and alleviate symptoms in keratitis.
Homeopathic Remedies for Keratitis
A few homeopathic cures can be considered for keratitis in view of the particular side effects and individual qualities of the patient. A few generally utilized cures include:
1. Aconitum Napellus: This treatment works well for keratitis that causes severe eye pain, inflammation, and light sensitivity. Stabbing or burning may be used to describe the pain.
2. Euphrasia: Euphrasia is a remedy that is frequently considered for keratitis that causes extensive eye tearing, burning, and itchiness. The eyes might have redness and swelling of the eyelids.
3. Pulsatilla: Keratitis that causes the sensation of a foreign object in the eye is treated with pulsatilla. The patient might have abundant tearing, and the side effects might move from one eye to the next.
4. Belladonna: In cases of severe eye pain, redness, and sensitivity to light, belladonna can be used. It may feel hot and throbbing in the eye.
5. Apis Mellifica: Apis Mellifica may be considered if the eye is swollen and puffy in addition to experiencing intense burning and stinging pain.
6. Arsenicum Album: Keratitis that causes burning and agitation, especially at night, may benefit from this remedy. The eyes might water plentifully.
7. Rhus Toxicodendron: Valuable for enlarged, red, oedematous eyes with corneal infusion and ulceration; regulated in 6C – 30C potencies, 3-5 pills, three times each day.
8. Mercurius Solubilis: Utilized for keratitis with painful, red and enlarged eyelids; managed in 2C – 30C potencies, 3-5 pills, three times each day.
If you want to find the best remedy and dosage for your particular situation, you should talk to a trained homeopath.
General Prevention of Keratitis
When it comes to keratitis, prevention is always better than treatment, and the following actions can help lower your risk:
1. Hand Hygiene: Wash your hands thoroughly before touching your eyes and avoid sharing personal items like towels or eye makeup to practice good hygiene.
2. Care for Contact Lenses: If you wear contact lenses, you should follow the right cleaning and storage guidelines. Before going swimming or sleeping, take them out.
3. Protective Eyewear: Wear protective eyewear whenever you participate in activities that could cause damage to the eyes, like playing sports or working with tools.
4. Stay away from Natural Triggers: Use shades to safeguard your eyes from UV light and goggles in dusty or blustery conditions.
5. Keep up with General Wellbeing: A solid way of life, including a decent eating regimen, physical activity, and sufficient rest, can reinforce your immunity system and diminish your vulnerability to infections.
6. Manage Underlying Health Conditions: If you have underlying health conditions that make you more likely to get keratitis, you should work with your doctor to effectively treat them.

Conclusion: Protect your Eyes!
The first step in protecting your vision from keratitis is understanding the condition, its causes, and potential risk factors. Keep in mind that homeopathy should always be administered under the supervision of a licensed homeopath as part of an all-encompassing strategy for treating keratitis.
If all else fails, talk with a medical care proficient who can direct you through the best strategy. By embracing preventive measures and looking for convenient clinical consideration, you can protect your eye wellbeing and diminish the gamble of keratitis. Protecting your eyes is a worthwhile endeavor because they serve as your windows to the outside world.
Reach out to us for a Consultation
For any queries, reach out to us at contact@homeopathic.ai
This blog is for information purposes. It’s crucial to note that while homeopathy is a centuries-old practice with many adherents worldwide, always consult a qualified homeopath or medical professional before initiating any treatment.