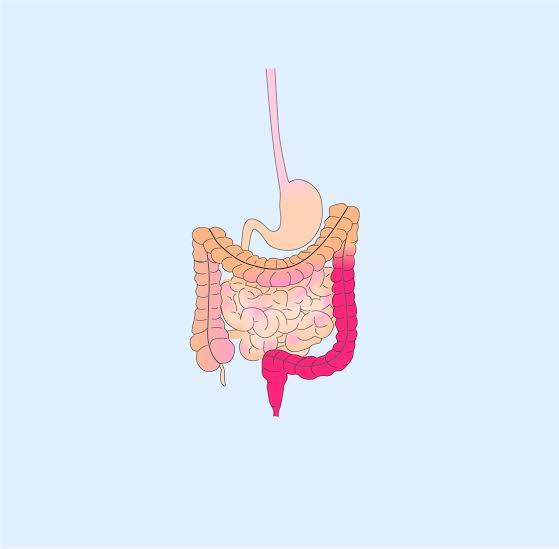
The colon and rectum are the main organs affected by the chronic inflammatory bowel illness ulcerative colitis. The inner lining of the large intestine has recurrent inflammation and ulcers, leading to symptoms such as diarrhea, bleeding in the rectal area, and stomach pain. To begin investigating therapy possibilities for those who are not familiar with this ailment, it is important to grasp the fundamentals.
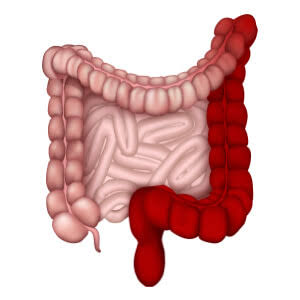
Pathology of Ulcerative Colitis
Usually, ulcerative colitis begins with inflammation in the rectum and progresses up into the colon. The inflammation mostly affects the colon’s interior lining, which can result in ulcers and a host of uncomfortable symptoms. As the inflammation worsens over time, there may be a greater chance of complications and long-term harm to the colon.
Delving into the Causes of Ulcerative Colitis
Although the precise origin of ulcerative colitis is yet unknown, the immune system, environmental, and genetic factors are thought to play a combined role. Further research is necessary to completely understand the precise causes of the illness, but some theories imply that it may be caused by an aberrant immunological response.
Risk Factors of Ulcerative Colitis
There are risk factors that can raise a person’s chance of getting ulcerative colitis. These variables include age, living situation, and even a family history of the illness. People who live in industrialised nations or in urban regions, for instance, are more likely to get the illness.
Signs and Symptoms of Ulcerative Colitis
Individual differences exist in the signs and symptoms of ulcerative colitis, which can range in severity from moderate to severe. Typical signs of the illness include the following:
Urgent and frequent bowel motions are referred to as diarrhea.
Lower abdominal pain, characterised by cramping and discomfort.
Stool bleeding, typically accompanied by pain, is known as rectal bleeding.
As a result of malabsorption and decreased food intake, weight loss can occur.
Fatigue caused by anaemia and inflammation.
In order to guarantee an accurate diagnosis and prompt treatment, it is imperative that you speak with a healthcare provider if you encounter any of these symptoms.
Investigating Ulcerative Colitis
In order to assess a patient who may have ulcerative colitis, medical professionals use a number of diagnostic procedures. These tests assist in establishing the severity of the ailment and verifying the diagnosis. Important experiments and conclusions consist of:
– Colonoscopy: A flexible tube equipped with a camera is used to visually inspect the colon.
– Biopsy: Gathering tissue samples in order to verify inflammation.
– Blood tests: To evaluate anaemia and inflammation.
– Stool Tests: To exclude bleeding and infections.
– Imaging: To assess problems, use techniques like CT scans or X-rays.
Determining the best course of action for therapy requires an understanding of the test results.
Distinguishing Ulcerative Colitis from Other Conditions
It is critical to differentiate ulcerative colitis from illnesses like Crohn’s disease and irritable bowel syndrome that present with comparable symptoms. Here’s how medical professionals distinguish between them:
– Colonoscopy and Biopsy: These aid in locating particular inflammatory patterns characteristic with ulcerative colitis.
– Clinical Presentation: Symptom severity and kind can frequently provide important information.
– Imaging: Studies using imaging may reveal distinguishing characteristics.
Effective treatment starts with a precise diagnosis.
General Management of Ulcerative Colitis
Usually, a combination of drugs, lifestyle changes, and occasionally surgical procedures are used to treat ulcerative colitis. Typical therapies consist of:
– Anti-Inflammatory Drugs: Aminosalicylates are one type of medication that reduces inflammation.
– Immunosuppressants: To manage an excessively reactive immune system.
– Biologics: Immune system modulation by targeted therapeutics.
– Surgery: The colon may need to be surgically removed in cases with extreme severity or problems.
The severity of the illness and each patient’s reaction to various treatments determine the course of treatment.
General Prevention of Ulcerative Colitis
Because ulcerative colitis is complicated and multifaceted, prevention is not always possible. You can, however, consider the following actions to lower your risk of problems and flare-ups:
– Medication Adherence: Taking your prescribed drugs as directed by your doctor.
– Nutritional Adjustments: Steer clear of trigger foods and keep your diet in balance.
– Stress Management: Lowering stress levels by practising relaxation methods and making lifestyle adjustments.
– Frequent Check-Ups: Maintaining a regular follow-up plan with your medical staff.
These techniques can aid those who suffer from ulcerative colitis in keeping a better handle on their illness.
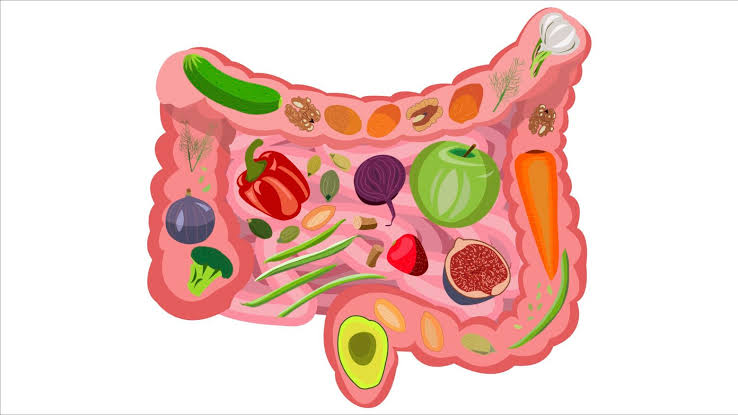
Ulcerative Colitis: Foods to Improve and Avoid
When it comes to treating ulcerative colitis, diet is crucial. Although dietary preferences might differ from person to person, the following are some basic recommendations for items to eat and avoid.
Foods that Help with Symptoms:
1. Fiber-Rich Foods: Foods high in soluble fiber, such as white rice, bananas, and oats, can help make stools more substantial.
2. Lean Proteins: Fish, poultry, and chicken supply vital nutrients without aggravating symptoms.
3. Probiotics: Fermented foods, yoghurt, and kefir can help maintain intestinal health.
Foods to Avoid:
1. Spicy Foods: These have the potential to aggravate the stomach.
2. High-Fiber Foods: During flare-ups, raw veggies, legumes, and whole grains can exacerbate symptoms.
3. Dairy Products: Dairy products might be problematic for ulcerative colitis sufferers because many of them are lactose intolerant.
Each person may react differently to particular foods, so it is important to speak with a medical expert or a qualified dietitian to develop a customized eating plan.
Exploring Homeopathy as a Complementary Approach
Although ulcerative colitis can be effectively managed with traditional medical therapy, some people look for complementary therapies like homeopathy to help them feel better. Homeopathy stimulates the body’s natural healing processes by using very diluted medicines, based on the “like cures like” theory.
It is important to explore homeopathy with your healthcare practitioner before deciding to use it as a treatment for ulcerative colitis. Since homeopathic treatments are customized, a qualified homeopath will evaluate your particular symptoms and requirements.
– Nux Vomica: Used to treat ulcerative colitis that worsens with mental strain, touch, spices, stimulants, and opiates, and that is accompanied by diarrhea after overindulgence, particularly in the morning. Recommended dosage: three times a day, three pills.
– Mercurius Corrosivus: Suitable for ulcerative colitis exhibiting dysentery-like symptoms, such as persistent tenesmus and hot, bloody, slimy, and foul feces. It is normally taken in 6C potency, which is 3-5 pills, three times a day, as symptoms intensify in the evening and at night.
– Phosphorus: For ulcerative colitis characterized by green mucus in the stool, excessive, incapacitating diarrhea, and weakness following bowel movements. Changes in weather and heated food or drink exacerbate symptoms. It is commonly taken in potencies ranging from 2C to 30C, as 3-5 tablets, three times a day.
– Aloes Socrotina: Taken into consideration when stools are watery and lumpy stools. It is frequently consumed in the summer, early in the morning, or during hot, dry weather. It is advised to take three pills, ranging in potency from 6C to 200C, three times a day.
Conclusion: A Healthy Colon is a Healthy You!
In conclusion, understanding ulcerative colitis, its causes, symptoms, and potential treatments is the first step in properly managing this condition. You can work toward enhancing your quality of life and reducing the interference that ulcerative colitis causes with your everyday activities by collaborating closely with your healthcare team, implementing any lifestyle changes that are required, and exploring complementary therapies like homeopathy. You can get advice from your healthcare practitioner on what choices are best for your overall health and wellbeing.
This blog is for information purposes. It’s crucial to note that while homeopathy is a centuries-old practice with many adherents worldwide, always consult a qualified homeopath or medical professional before initiating any treatment.
For any queries, reach out to us at contact@homeopathic.ai