Epididymitis is a condition that can be awkward and troubling for men, however with the right information and approach, it tends to be forestalled. In this guide, we will investigate epididymitis exhaustively, from its definition and pathology to its different sorts, stages, causes, and risk elements. In addition, we will discuss its signs and symptoms, its general management, investigations, and the possibility that homeopathy can help treat this condition. Together, let’s set out on this educational journey.
What is Epididymitis?
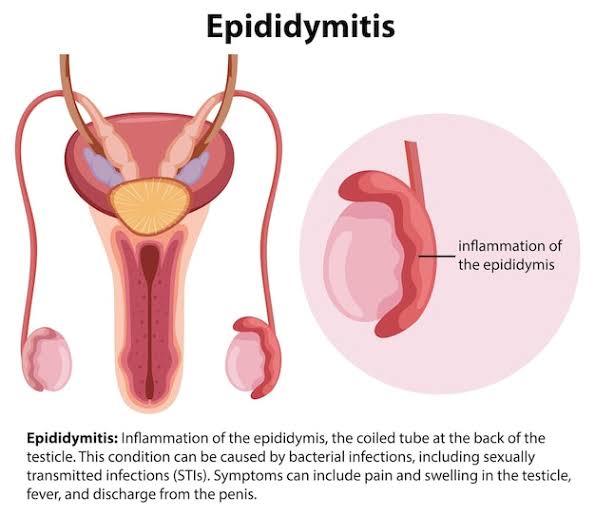
Epididymitis alludes to the irritation or swelling of the epididymis, a snaked tube situated at the rear of the gonad. The epididymis assumes a vital part in putting away and shipping sperm. At the point when it becomes aroused, it can cause torment, inconvenience, and different side effects.
The Pathology of Epididymitis
The essential pathology of epididymitis is infection. It typically occurs when sexually transmitted infections (STIs) or urinary tract bacteria spread to the epididymis. The epididymis becomes inflamed and swollen due to this infection.
The Types of Epididymitis
Epididymitis can be divided into two main categories:
1. Acute Epididymitis: This is a severe, sudden form of the condition that is frequently brought on by a bacterial infection. It prompts fast beginning of side effects and requires brief clinical consideration.
2. Chronic Epididymitis: Chronic Epididymitis is described by tireless or intermittent side effects that keep going on for a very long time or even months. It could be brought on by an ongoing infection of a low grade or by other underlying issues.
The Stages of Epididymitis
There are three stages of epididymitis:
1. The inflammation and symptoms are at their peak during the acute stage. Common symptoms include fever, swelling, and pain.
2. The subacute stage begins as soon as the acute symptoms start to go away, but it may not completely disappear. There may still be some discomfort.
3. Long-term or recurrent symptoms are characteristic of the chronic stage of epididymitis. A person’s quality of life can be significantly impacted.
Causes of Epididymitis
– Bacterial Infections: Bacterial infections are the most common cause of epididymitis. Urinary tract infections (UTIs) or the spread of bacteria from STIs like chlamydia or gonorrhea can cause these infections.
– Non-Bacterial Causes: Epididymitis can also be brought on by trauma, surgery, or urine reflux into the epididymis.
Risk Factors for Epididymitis
– Sexual Activity: Having multiple partners and engaging in sexual activity raises one’s risk of contracting sexually transmitted infections (STIs) that can result in epididymitis.
– Problems with the Urine: Problems with the urinary tract, like urethral strictures or an enlarged prostate, can make it more likely that you will get epididymitis and then have urinary reflux.
– Unprotected Sex: Not using condoms while having sex can make you more likely to get sexually transmitted infections (STIs).
Signs and Symptoms of Epididymitis
The signs and side effects of epididymitis can change contingent upon the stage and seriousness of the condition. Some typical signs include:
– Testicular Pain: In most cases, the pain starts in just one testicle and can spread to the groin and lower abdomen.
– Swelling: The affected epididymis and testicle may appear to be swollen.
– Redness and warmth: The scrotal region may turn red and feel warm to the touch.
– Fever and chills: Fever and chills may occur in acute cases.
– Urinary Pain: When they urinate, some people with epididymitis may feel pain or discomfort.
– Discharge: If an STI is the cause of epididymitis, the penis may also discharge.
General Management of Epididymitis
Epididymitis typically responds well to a combination of medical care and self-care. What you can do is:
– Anti-infection agents: In the event that the reason is bacterial infection, your PCP will endorse anti-microbials to treat the infection.
– Help with discomfort: Over-the-counter pain killers like ibuprofen can assist with easing inconvenience.
– Rest and Elevation: Swelling and pain can be reduced by resting and elevating your scrotum.
– Strong Clothing: Wearing good underwear can give extra solace.
– Hydration: Maintaining adequate hydration can aid in the infection’s elimination.
Investigations of Epididymitis
The following tests may be performed by your healthcare provider to diagnose epididymitis and determine its underlying cause:
– Physical Assessment: An exhaustive assessment of the scrotum and gonads to survey swelling, delicacy, and other signs.
– Urine and Blood Tests: These tests can assist with recognizing the presence of infection or aggravation.
– Ultrasound: An ultrasound can give definite pictures of the scrotum, assisting with precluding different circumstances and affirm epididymitis.
– Testing for STIs: If STIs are suspected, chlamydia and gonorrhea tests may be performed.
The Role of Homeopathy in Treating Epididymitis
Here are a few homeopathic remedies that are commonly used for epididymitis:
1. Rhododendron: Rhododendron is shown when there is testicular swelling and pain, particularly on the left side, and it could be drawn up. It can also be used to treat testicular induration and swelling following gonorrhea.
2. Spongia Tosta: Swelling of the spermatic cord and testicles, accompanied by pain and tenderness, is treated with spongia tosta. It is normally utilized for orchitis and epididymitis.
3. Apis Mellifica: Apis Mellifica is reasonable when there is pain and swelling of the testicles and prostate. It is well-known for its pain in the affected area that is stinging and pinching.
4. Clematis Erecta: Clematis Erecta is used to treat drawing pains in the testes and spermatic cord and swelling of the right half of the scrotum. Scrotum thickening and painful inflammation may benefit from its use.
5. Mercurius Solubilis: Mercurius Solubilis is used to treat genital itchiness, tingling, and shooting. It is well-known for reducing testicular and prepuce swelling, redness, and burning pain.
6. Cantharis: Cantharis is used for Epididymitis when urination causes a burning pain.
7. Pulsatilla: Pulsatilla may be a possibility if the scrotum feels heavy and the pain is changing.
8. Arnica: If the pain is caused by an injury or trauma, arnica can be helpful.
Conclusion: Let’s Talk About Men!
In conclusion, epididymitis is a condition that can be uncomfortable and distressing, but with the right information and treatment, it can be effectively managed and even avoided. For early diagnosis and treatment, it is essential to have an understanding of its definition, pathology, types, stages, causes, and risk factors. It is essential to recognize the symptoms and seek prompt medical attention.
When deciding on the best course of action for your particular situation, you should always speak with a trained medical professional. You can live a healthier and more comfortable life while lowering your risk of epididymitis by taking preventative measures and maintaining good urological health. Remember that your health and well-being should always come first, and getting help from a professional is essential to a speedy recovery.
Reach out to us for a Consultation
For any queries, reach out to us at contact@homeopathic.ai
This blog is for information purposes. It’s crucial to note that while homeopathy is a centuries-old practice with many adherents worldwide, always consult a qualified homeopath or medical professional before initiating any treatment.